状态模式,当一个对象的内在状态改变时允许改变其行为,这个对象看起来像是改变了其类。
状态模式可以将复杂的判断逻辑简化,将庞大的判断逻辑分隔开,对单个判断的修改不会影响到其他判断。并且在客户端调用时,也只需要执行Context向外暴露的类即可,不需要知道到底有多少判断逻辑。
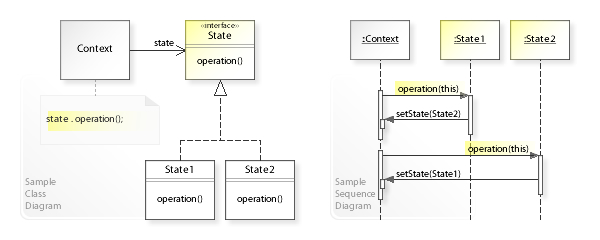
State类
interface State {
void writeName(StateContext context, String name);
}
class LowerCaseState implements State {
@Override
public void writeName(StateContext context, String name) {
System.out.println(name.toLowerCase());
context.setState(new MultipleUpperCaseState());
}
}
class MultipleUpperCaseState implements State {
/* Counter local to this state */
private int count = 0;
@Override
public void writeName(StateContext context, String name) {
System.out.println(name.toUpperCase());
/* Change state after StateMultipleUpperCase's writeName() gets invoked twice */
if (++count > 1) {
context.setState(new LowerCaseState());
}
}
}
context类
class StateContext {
private State state;
public StateContext() {
state = new LowerCaseState();
}
/**
* Set the current state.
* Normally only called by classes implementing the State interface.
* @param newState the new state of this context
*/
void setState(State newState) {
state = newState;
}
public void writeName(String name) {
state.writeName(this, name);
}
}
客户端代码
public class StateDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StateContext context = new StateContext();
context.writeName("Monday");
context.writeName("Tuesday");
context.writeName("Wednesday");
context.writeName("Thursday");
context.writeName("Friday");
context.writeName("Saturday");
context.writeName("Sunday");
}
}
最后展示内容
monday
TUESDAY
WEDNESDAY
thursday
FRIDAY
SATURDAY
sunday
